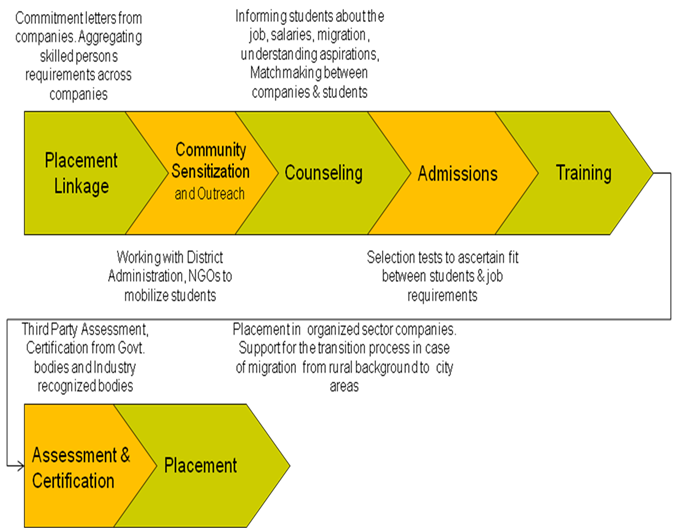
Training Delivery methodology considerations occur after we've
defined the objectives, assessments, content types, and learning sequence for
the training. Depending on objectives and the content types, some — or even all
— of training can be done outside of the classroom Or a mix of training methods
can be used to make training effective.
Blended training combines various types of training and information
communication to achieve the most effective performance gains in the most
efficient manner. Following are the methodology t hat we are using in our
classroom:
- Instructor-led classroom-based
training: An interactive,
instructor-led approach where the instructor and trainees meet in a
classroom for a specific duration of time.
- Multimedia-based training (MBT): Interactive training presented
through audio-visual using a
variety of multimedia CD ROM, Speakers, Projector, Headphones etc.
- Reference study material: Information includes training aids
workbooks, charts, posters, user manuals, and reference guides.
Using a variety of methods during an orientation or
training helps get your messages across and holds participant interest. Varying
the methodology can make a session more interactive, interesting, and fun. The
following chart lists some suggested methods and their uses. All of these
instructional techniques have benefits. The choice of a method depends on the
objectives of a particular session, the characteristics of the learners, and
the time and resources available
|
Method |
Ideal for |
Methods |
Other consideration |
|
Brainstorming |
·
Allowing hands-on experiences ·
Entering and learning about a new environment ·
Engaging participants |
·
Form group ·
Assign topic ·
Give appropriate time ·
See the outcome ·
Feedback
|
·
Field trips can be used in a wide variety of
places and for different topics. ·
Field trips provide an opportunity to
experience first-hand an actual environment or situation and enter it safely
with guidance. |
|
Games |
·
Practicing skills while having fun ·
Allowing real-life application of skills ·
Teaching skills ·
Engaging participants |
·
Form groups ·
Define the objective of activity ·
Tell how to follow the process of game ·
Give time limit ·
Move around the group while they are
preparing performing ·
feedback |
·
Games provide the opportunity for
participants to enjoy learning. ·
General games can be adapted to use questions
that refer to your topic. ·
Be sure that the games you use do not offend
participants by seeming childish (e.g., by using graphics aimed at children). |
|
Lectures |
·
Conveying a lot of information in a short
period of time ·
Briefly introducing a topic ·
Presenting basic information ·
Imparting knowledge |
·
Define the topic & objective ·
Use visuals, examples & anecdotes ·
Keep trainees involve by asking question
|
·
Some groups may initially be more receptive
to lectures than to hands-on activities. ·
Lectures may not lead to actual learning, as
participants are passive observers and do not have the opportunity to apply
learning. ·
Lectures can be more effective when preceding
or following another method. ·
Lectures are more interesting when combined
with visuals, examples, and anecdotes, and when open-ended questions are
encouraged |
|
Parking Lot |
·
Deferring irrelevant questions or those the
trainer doesn’t have time to address immediately ·
Demonstrating that the trainer will follow up
on unanswered questions |
·
The instructor should always welcome
questions from learners draw a simple
“parking lot” on flip chart paper post it in the room
where participants will have easy access, preferably near the door ·
Instruct them to write down any question they
may have on the Post-It during the class. During a break, post their question
in the parking lot and it will be answered during the class. |
·
On the wall, hang flipchart labeled “Parking
Lot.” ·
When questions that cannot be answered arise,
write them on the flipchart. ·
If you do not know the answer, be `honest,
get back to the participants later with the information. ·
This technique will encourage the learner to
ask questions during class |
|
Role Plays |
·
Dramatizing a problem or situation ·
Identifying possible solutions ·
Engaging participants prior to a discussion ·
Teaching skills |
·
Make the groups ·
Clear the objective of activity ·
Give scenario to all the groups ·
Assign time for preparation ·
Assign time for play ·
if the role play has degraded into something
or silly or irrelevant to the discussion, the facilitator can the step in and
call the role play off ·
feed back ·
Open discussion/Question answer |
·
Participants assume a role and act out a
situation with their group while other participants observe ·
Role-plays are effective for helping
participants practice skills or experience situations, and then discussing
them. ·
It is extremely important to debrief and
reflect after a role play ·
There is no right or wrong way to perform a
role-play, as long as mutual respect is maintained. |
|
Videos |
·
Providing visuals ·
Using with guided discussion |
·
Show the relevant video ·
Ask question about their understanding ·
Discussion too can take place ·
feedback |
·
Information can be conveyed in an interesting
manner. ·
A useful technique is to pause the video and
ask participants to discuss what they have seen, predict what might happen
next, and relate the topic to real-life situations. |
training value chain